Recent years have brought unusually high temperatures to the world’s waters—and with them, major impacts on marine life and coastal communities. However, since early 2023, this trend has significantly intensified, with each day for more than a year setting a new record high.
Several factors have likely contributed to these temperature increases—including rising greenhouse-gas levels creating excess atmospheric warming that absorbs into the world’s oceans—but climate scientists are having trouble completely explaining the anomalous warming. Some point to international fuel standards implemented in 2020 that reduced container ship aerosol pollution and the cooling effect that comes with it. Others attribute some of the rise to natural occurrences such as the underwater Hunga Tonga-Hunga Haʻapai volcano eruption in 2022 that sent up plumes of water vapor into the upper atmosphere that absorbs heat radiated from Earth and prevents it from escaping out to space.
The effects have created eye-popping weather and climate events in recent years. In early 2023, waters off the coast of South Florida reached more than 100 degrees—approximately the temperature of the water in a hot tub. Coral reefs have begun to experience bleaching at levels previously thought impossible, endangering one of the most important ecosystems for marine life. Hurricanes Lee and Otis last year became some of the fastest-intensifying storms in recorded history on their way to Category 5 strength, and the 2024 hurricane season is projected to be one of the most active on record.
Changes in Global Sea Water Temperature Over Time
In February 2024, ocean temperatures reached the highest level on record
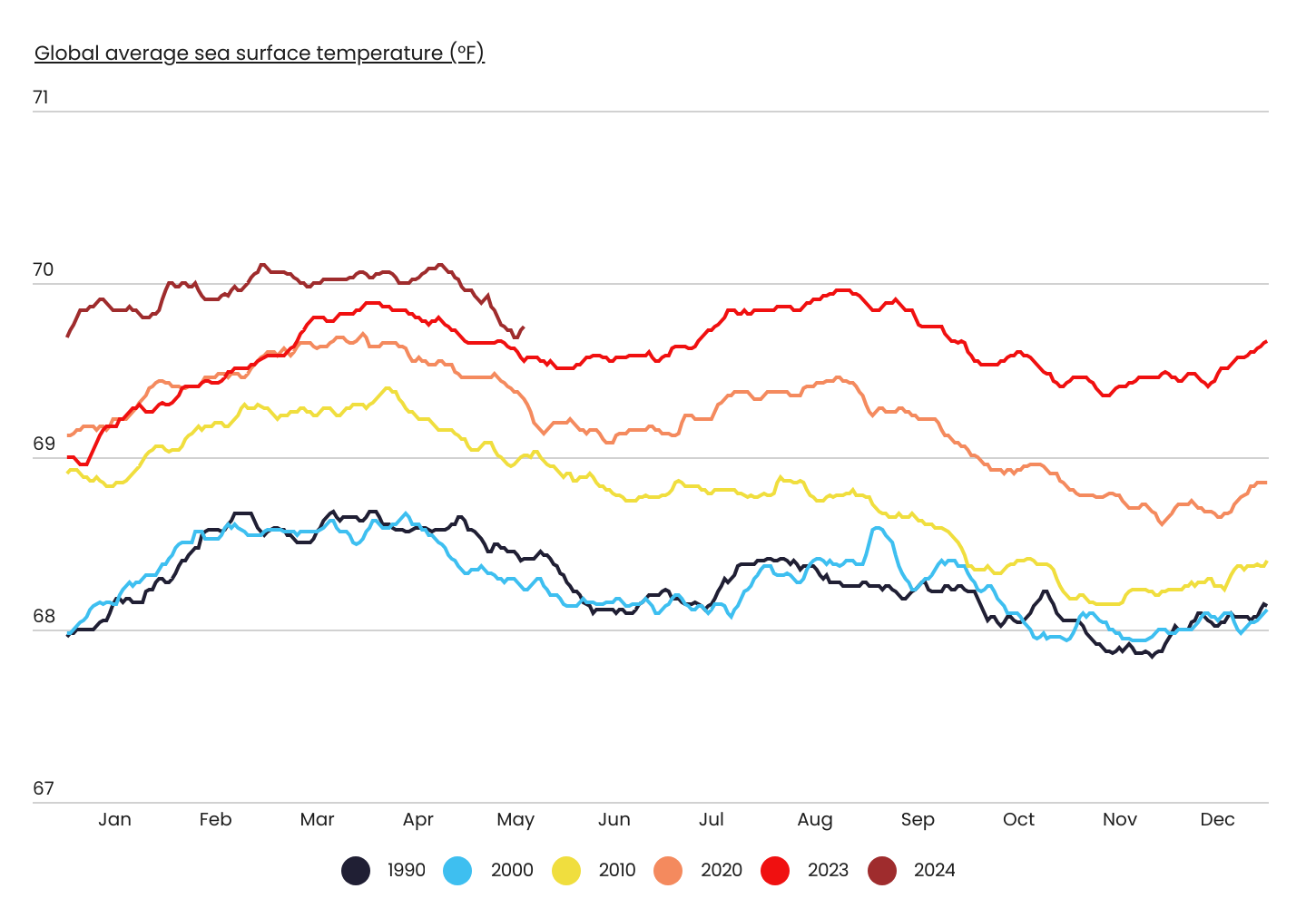
Source: Captain Experiences analysis of the University of Maine’s Climate Change Institute data
On February 29, 2024, the average global sea surface temperature reached a new daily high of 70.1 degrees Fahrenheit, highlighting the accelerating warming trend. Compared to previous decades, sea surface temperatures have been rising much faster each year. For example, the average ocean temperatures in 1990 and 2000 were extremely similar. However, by 2010, daily ocean temperatures exceeded those of 2000 by an average of 0.5 degrees Fahrenheit. In 2020, daily temperatures further surpassed those of 2010 by an average of 0.4 degrees Fahrenheit. And in just three years, average ocean temperatures in 2023 exceeded those of 2020 by another 0.4 degrees.
While the pace of change is alarming, the effects of these trends are not evenly distributed geographically. For coastal communities in the U.S., that means that some areas are more likely to be exposed to rising water temperatures than others. Communities that have experienced rapid increases in water temperatures may find themselves more vulnerable to extreme weather events—and with them, risks of extensive property damage, diminished economic activity, and the loss of human life.
Changes in Coastal Water Temperature by Location
The Gulf Coast saw the largest summer water temperature increases over the past decade
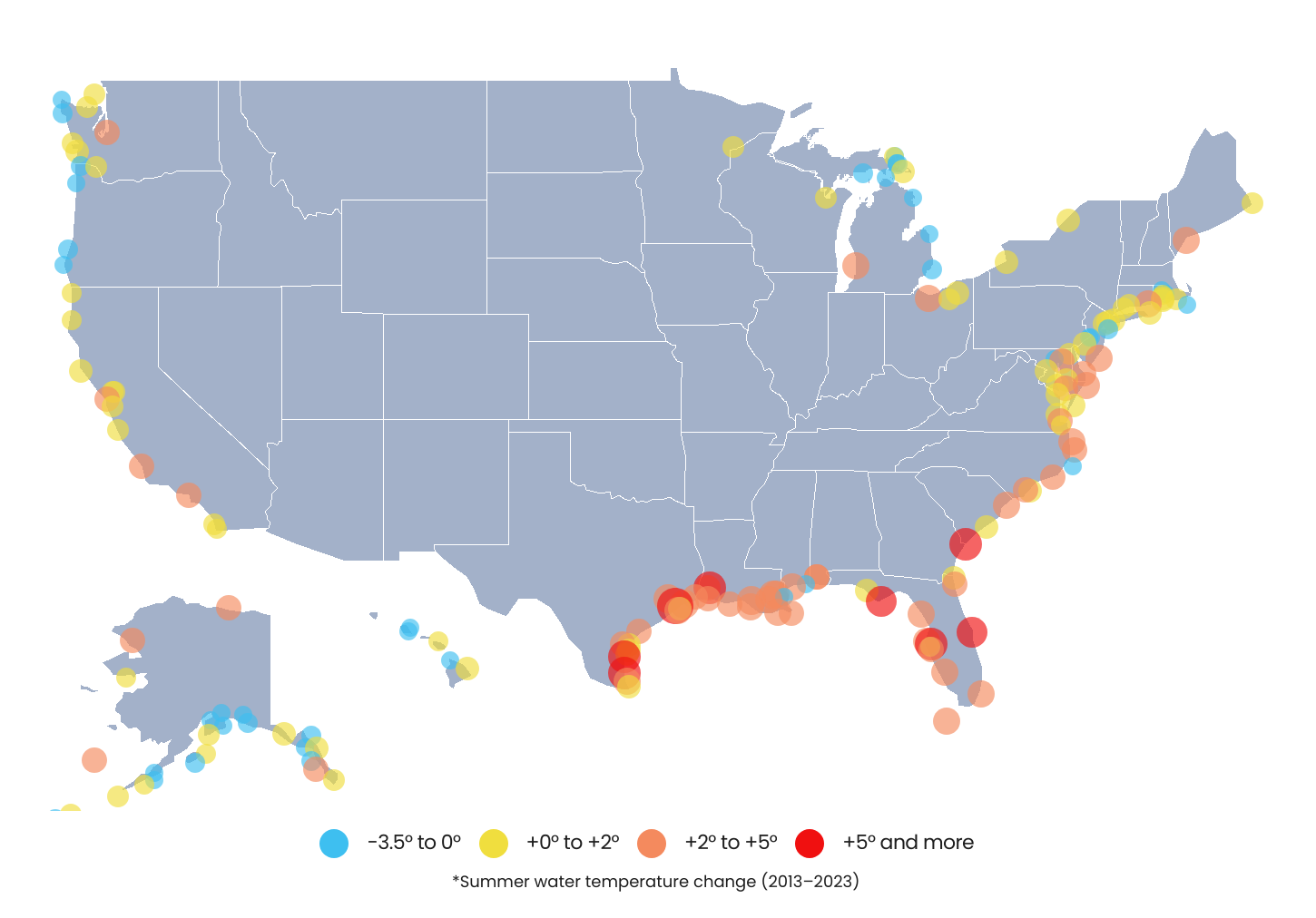
Source: Captain Experiences analysis of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Tides and Currents data
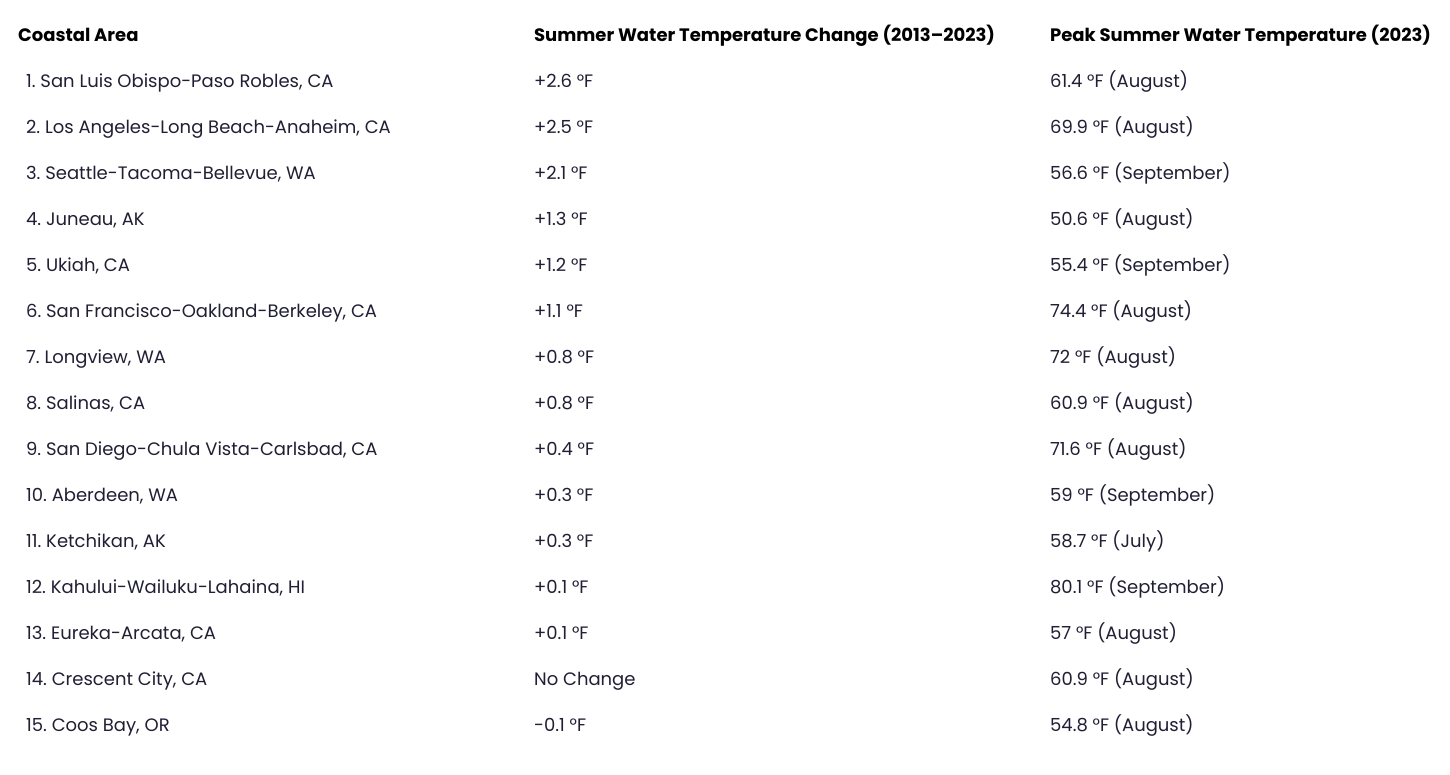
In the U.S., concerns are greatest for residents living near the Gulf of Mexico in states like Texas, Louisiana, and Florida. Over the last decade, the Gulf Coast has seen the greatest increase in water temperatures as measured in the summer, led by the Raymondville area in Texas with a 6.5 degree increase. In contrast, many locations in the Pacific Coast, northern Atlantic Coast, and Great Lakes regions saw minimal increases—or in some cases, declines—in summer surface water temperatures between 2013 and 2023.
The analysis was conducted by researchers at Captain Experiences, an online platform that helps people find and book fishing and hunting trips, using data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Below is a breakdown of the coastal areas that saw the biggest increase in summer water temperature over the last 10 years. For complete results, see Coastal Areas That Saw the Biggest Increase in Water Temperature on Captain Experiences.
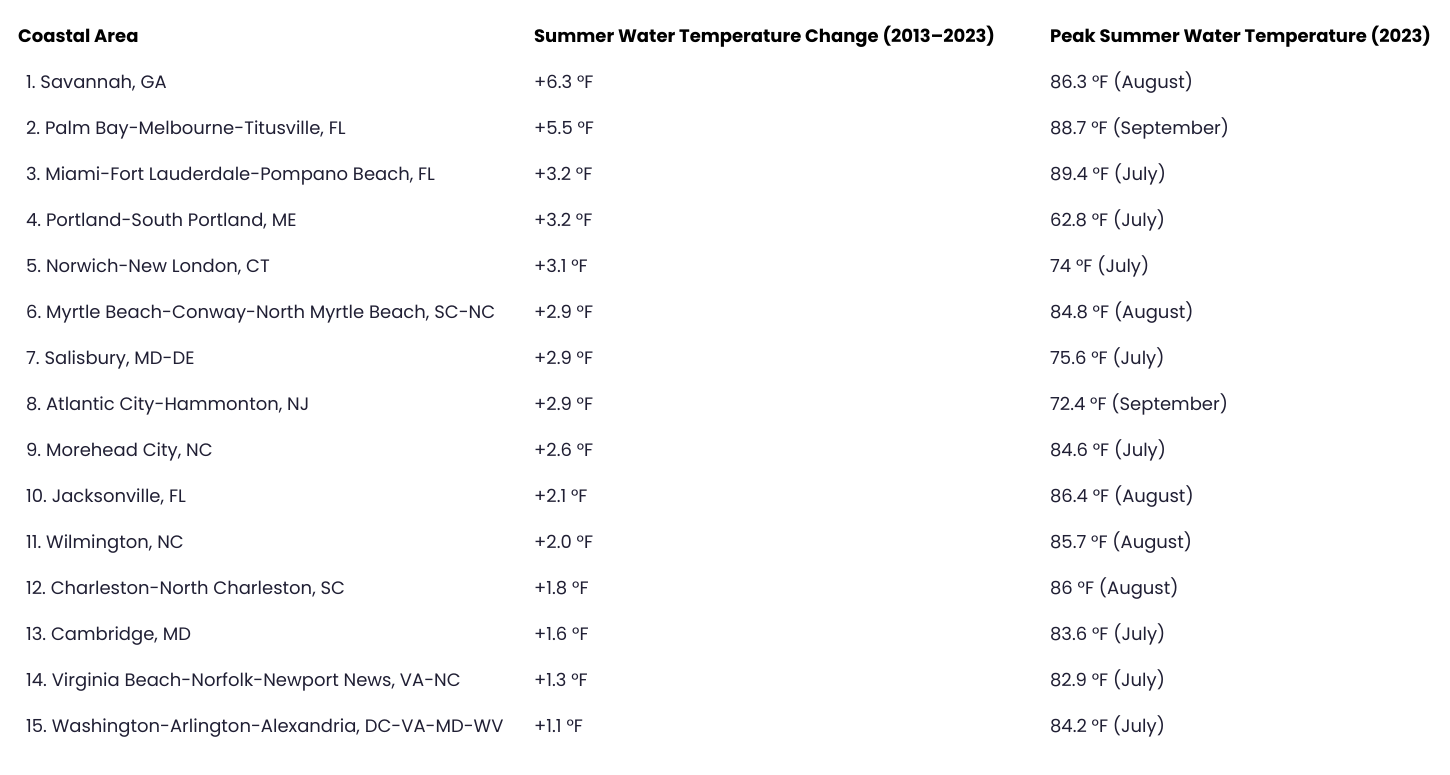
Atlantic Coast Metros That Saw the Biggest Increase in Water Temperature
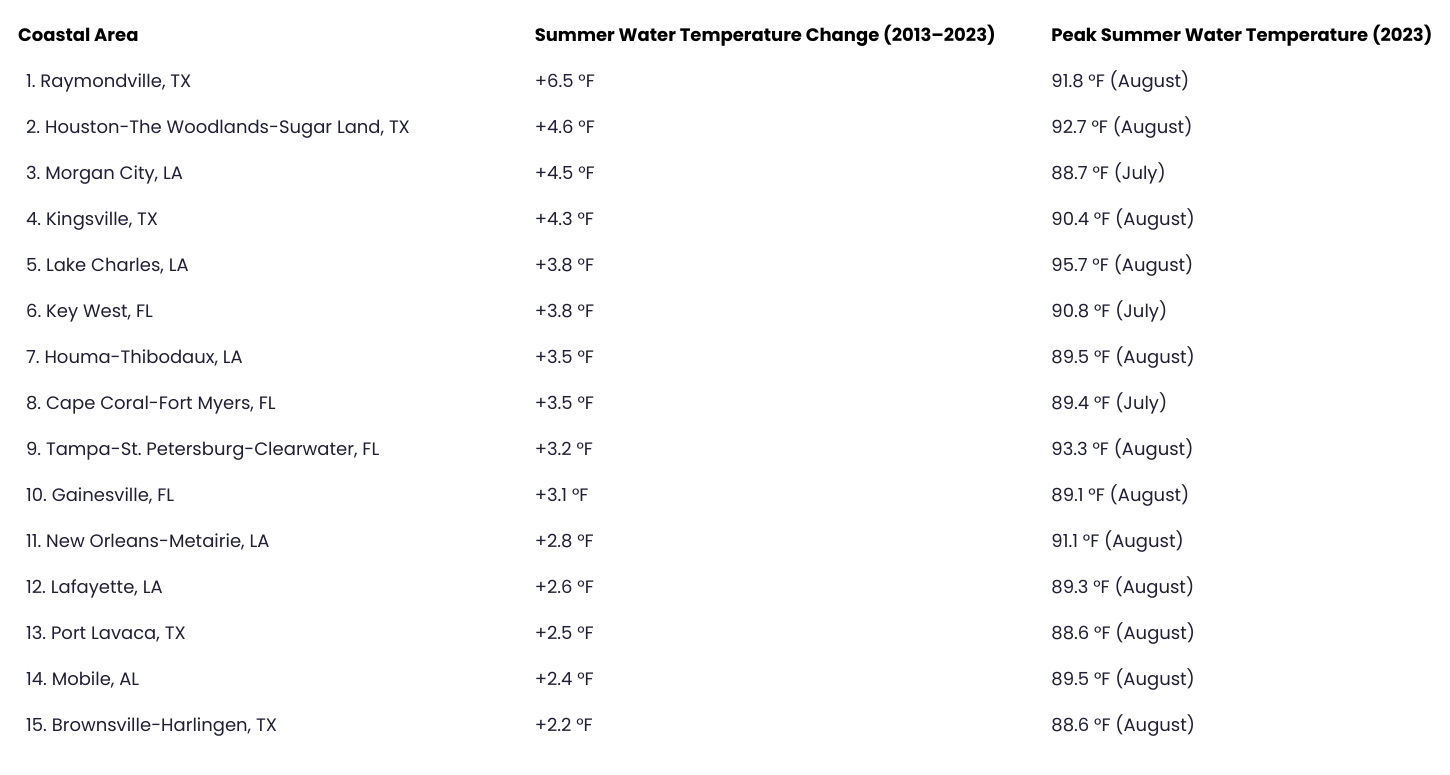
Gulf Coast Metros That Saw the Biggest Increase in Water Temperature
Great Lakes Metros That Saw the Biggest Increase in Water Temperature

Pacific Coast Metros That Saw the Biggest Increase in Water Temperature
Methodology & Detailed Findings

Photo Credit: Shamiso Chikanga / Shutterstock
The data used in this study is from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Tides and Currents series. To determine the coastal areas that saw the biggest increase in water temperature, researchers at Captain Experiences calculated the average summer water temperature change from 2013 to 2023 across each coastal metropolitan and micropolitan area. Average summer water temperatures were calculated by averaging hourly surface water temperatures for July, August, and September, and peak summer water temperatures were calculated using the largest average monthly water temperature for any given meteorological or physical oceanographical station located within each coastal area. Additionally, only metropolitan and micropolitan areas with sufficient coastal sea water temperature data were included.
For complete results, see Coastal Areas That Saw the Largest Increase in Water Temps on Captain Experiences.
